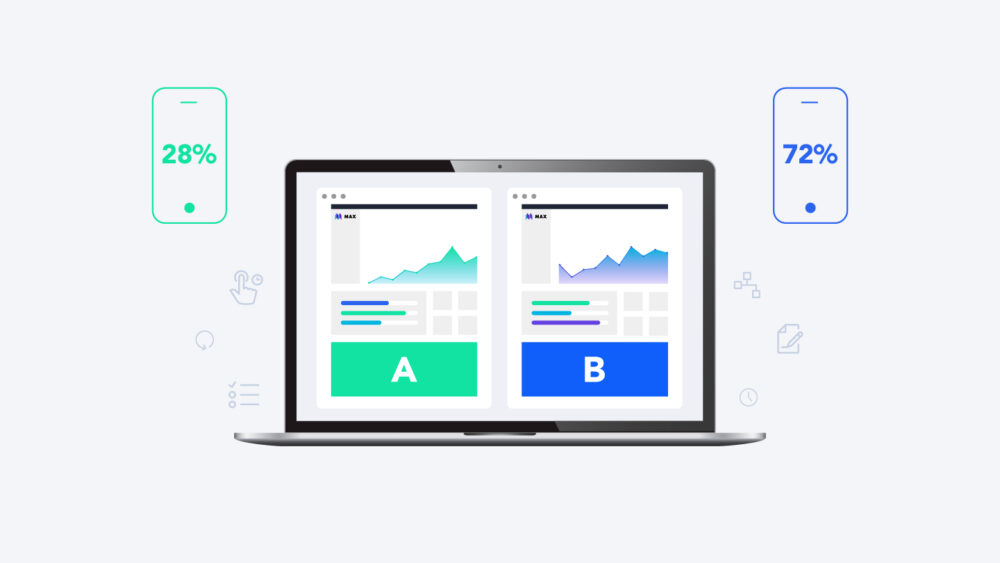
Introduction
As a Product Design Manager, enhancing product performance is one of the core missions of our role. To achieve this goal, we must prioritise user experience (UX) activities that deliver the highest return on investment (ROI).
In this article, we will explore the top 10 UX activities that have proven to be the most impactful in improving product performance.
From A/B testing to user interviews, each activity plays a critical role in optimising the user experience and driving tangible results for our products.
1. A/B Testing: Unleashing Data-Backed Insights
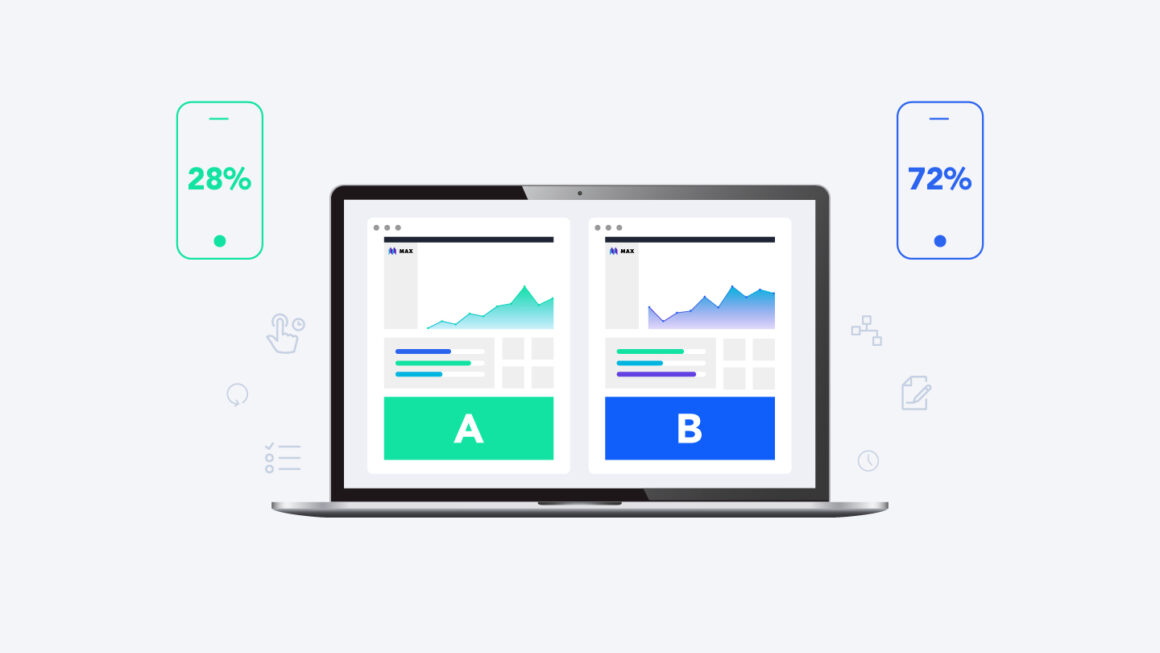

A/B testing is a powerful UX activity that allows us to compare different design variations and identify what resonates best with users.
By testing different layouts, features, and call-to-action buttons, we gain data-backed insights to make informed design decisions that maximise conversions and engagement.
Pros:
- Provides concrete data to support design decisions.
- Helps identify the most effective design variations.
- Enables iterative improvement for better conversions.
Cons:
- Requires significant traffic or user base for meaningful results.
- May not uncover qualitative user insights.
2. User Testing: Uncovering User Behaviour Patterns
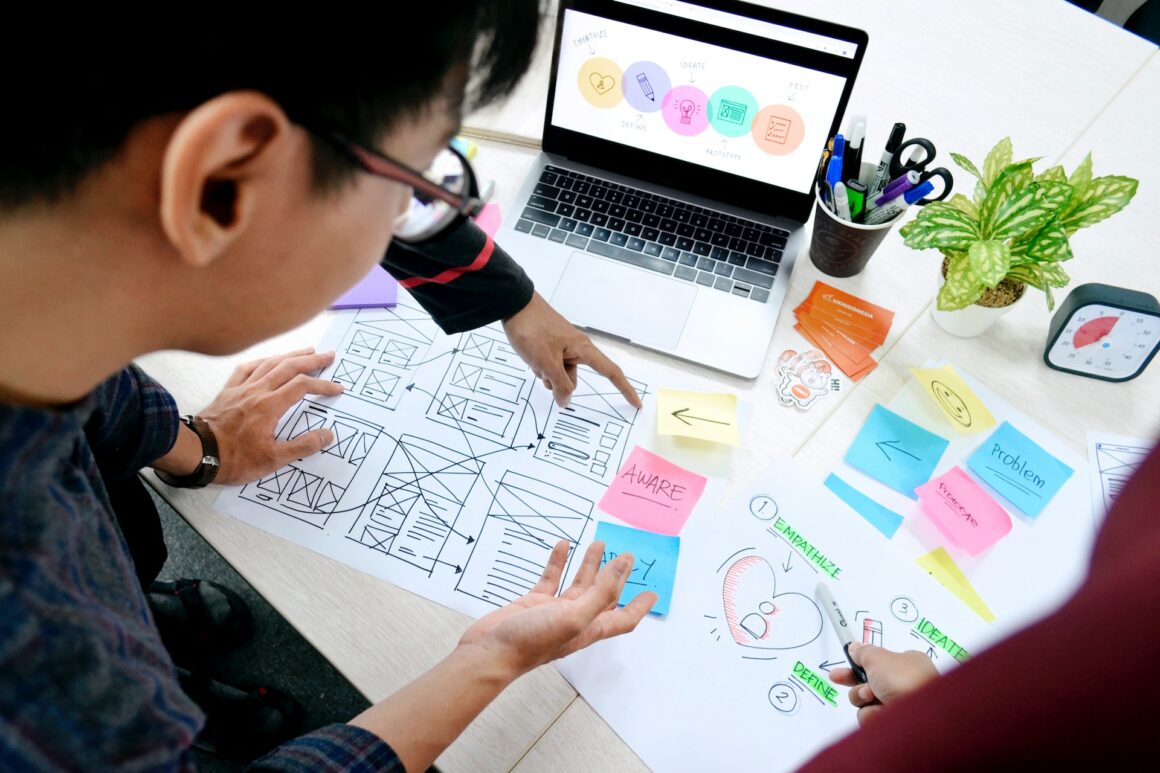

User testing is essential for understanding how real users interact with our products. By observing users navigate through prototypes or live websites, we gain valuable insights into their behaviour, pain points, and preferences.
These insights guide us in refining the user experience and addressing usability issues.
Pros:
- Gathers authentic user feedback through direct observation.
- Uncovers usability issues and pain points.
- Validates design assumptions and hypotheses.
Cons:
- Can be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Limited sample size may not represent the entire user base.
3. User Interviews: Delving into User Needs

User interviews provide an opportunity to directly engage with users and uncover their needs, motivations, and pain points.
Through empathetic conversations, we gain deep insights into user perspectives, enabling us to tailor our product to better meet their expectations.
Pros:
- Provides in-depth understanding of user motivations and expectations.
- Offers qualitative insights to complement quantitative data.
- Builds empathy and strengthens user-centric design.
Cons:
- Requires skilled interviewers to extract valuable insights.
- Limited to the availability of willing participants.
4. Polls and Surveys: Gathering Quick Feedback

Polls and surveys are quick and effective methods to gather user feedback at scale. By asking targeted questions, we obtain valuable insights on user preferences, satisfaction, and pain points.
This data helps us prioritise improvements and align our product with user expectations.
Pros:
- Efficiently collects data from a large user base.
- Allows for quick validation of design hypotheses.
- Provides insights on user preferences and pain points.
Cons:
- Responses may lack context or depth.
- Response bias can skew results.
5. Usability Heuristics Evaluation: Identifying Usability Gaps

Conducting usability heuristics evaluations allows us to assess our product’s compliance with established usability principles.
This activity helps us identify usability gaps and areas of improvement, leading to enhanced user satisfaction and reduced friction.
Pros:
- Evaluates designs against established usability principles.
- Identifies critical usability issues early in the design process.
- Offers a standardised framework for evaluation.
Cons:
- May not address specific user needs.
- Requires expertise in usability principles.
6. Click Heatmaps and Session Recordings: Visualising User Interactions
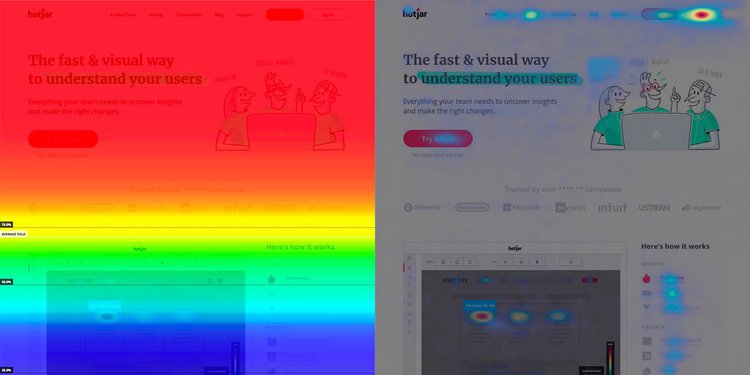
Click heatmaps and session recordings provide visual representations of user interactions on our website or app.
By understanding user behaviour patterns, we can optimise user flow, design, and content placement to drive desired actions.
Pros:
- Provides visual representation of user engagement and behavior.
- Identifies popular and underutilised areas of the product.
- Helps optimise UI design and user flow.
Cons:
- Requires appropriate tools and analytics setup.
- Lacks context on user intent or motivation.
7. Persona Development: Designing for User Segments
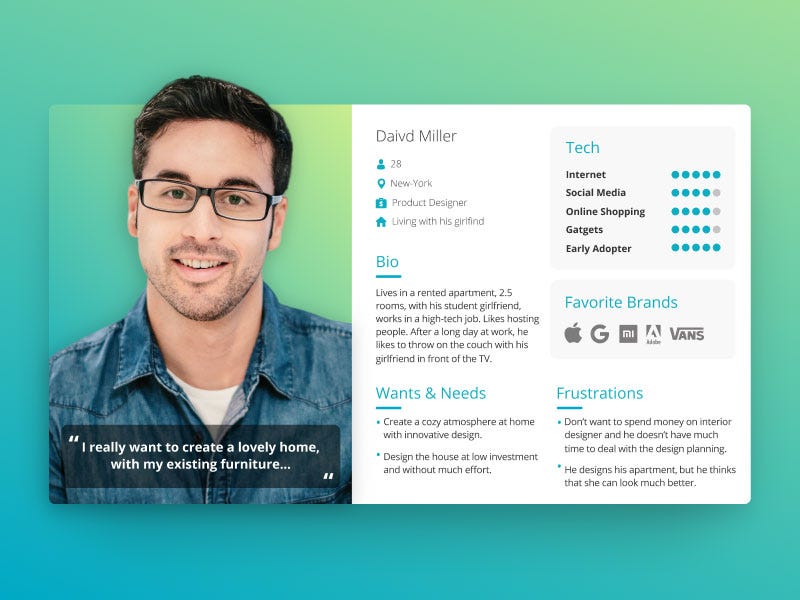
Persona development involves creating representative user profiles based on research data.
By understanding different user segments, we can tailor our product design to cater to specific user needs and preferences.
Pros:
- Creates a shared understanding of target users.
- Guides design decisions based on user needs and goals.
- Facilitates empathy-driven design.
Cons:
- Building accurate personas requires comprehensive user research.
- May oversimplify user diversity within segments.
8. Information Architecture (IA) Evaluation: Streamlining Navigation
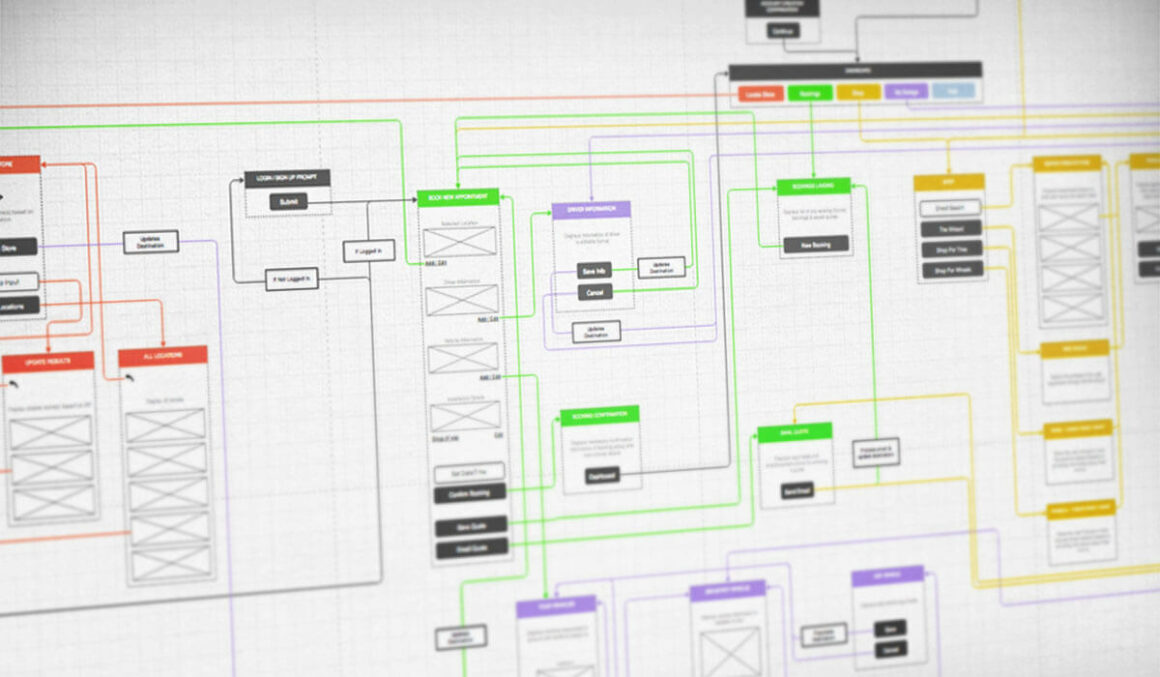
Evaluating the information architecture of our product ensures a clear and intuitive navigation experience for users.
Pros:
- Improves findability and navigation within the product.
- Reduces user frustration and enhances user satisfaction.
- Enhances overall user experience.
Cons:
- May require significant restructuring for established products.
- Could lead to resistance from stakeholders.
An organised and efficient IA reduces user frustration and helps users find what they need quickly.
9. Performance Optimisation: Enhancing Speed and Efficiency
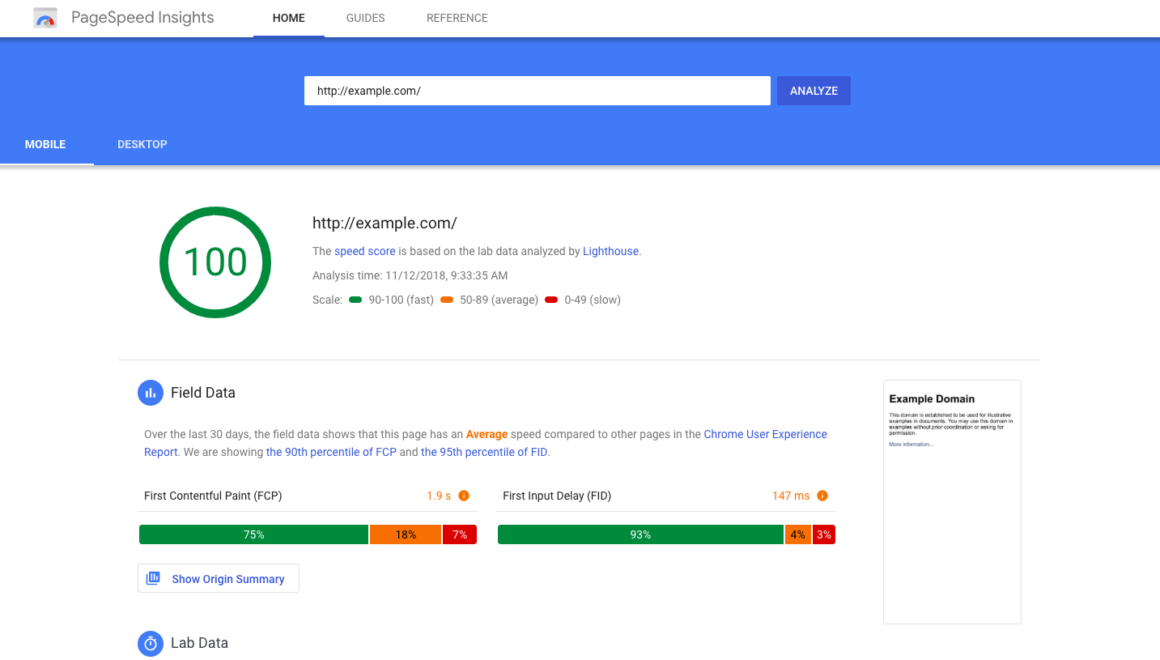
Performance optimisation is crucial for ensuring our product loads quickly and performs efficiently.
Faster loading times and smoother interactions lead to improved user satisfaction and increased engagement.
Pros:
- Increases user satisfaction and engagement.
- Reduces bounce rates and improves conversion rates.
- Impacts search engine rankings positively.
Cons:
- Can be technically complex and resource-intensive.
- Balancing performance and design aesthetics can be challenging.
10. Accessibility Audits: Designing for All Users

Conducting accessibility audits ensures our product is inclusive and accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
By adhering to accessibility standards, we expand our user base and demonstrate our commitment to inclusivity.
Pros:
- Demonstrates commitment to inclusivity and diversity.
- Expands the user base to reach users with disabilities.
- Aligns with legal requirements for accessibility.
Cons:
- Requires in-depth knowledge of accessibility guidelines.
- Implementing changes may require development resources.
Conclusion
As Product Design Managers, our pursuit of optimiing product performance is fuelled by strategic and data-driven UX activities.
By investing in A/B testing, user testing, interviews, polls, and other high ROI-driven activities, we align our efforts with user needs and preferences.
Utilising the insights gained from these activities, we refine the user experience, drive meaningful results, and create products that stand out in the competitive landscape.